box-cox-t distribution In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution. It is a continuous probability distribution having probability density function (pdf) given by for y > 0, where m is the location parameter of the distribution, s is the dispersion, ƒ is the family . Find Metal utility hooks & racks at Lowe's today. Shop utility hooks & racks and a variety of storage & organization products online at Lowes.com.
0 · doubly stochastic poisson process
1 · cox regression equation
2 · box cox vs johnson transformation
3 · box cox transformation negative values
4 · box cox transformation lambda values
5 · box cox plot interpretation
6 · box cox normal distribution
7 · box cox lambda meaning
Majority of greenhouse shelves are made from metals like aluminum and steel because they are functional, durable (especially in humid conditions because they are resistant to oxidation), and easy to transport (easy to move around when the plants start growing).
In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution. It is a continuous probability distribution having probability density function (pdf) given by for y > 0, where m is the location parameter of the distribution, s is the dispersion, ƒ is the family .
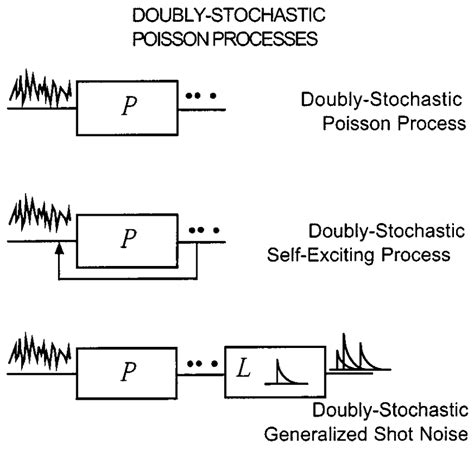
Extra distributions can be created, by transforming, any continuous distribution defined on the real line, to a distribution defined on ranges 0 to infinity or 0 to 1, by using a ’log’ or a ’logit’ . BCT() returns a gamlss.family object which can be used to fit a Box Cox-t distribution in the gamlss() function. dBCT() gives the density, pBCT() gives the distribution . The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. The Box–Cox t (BCT) distribution is presented as a model for a dependent variable Y exhibiting both skewness and leptokurtosis. The distribution is defined by a power transformation Y ν.
The Box-Cox t (BCT) distribution is presented as a model for a dependent variable Y exhibiting both skewness and leptokurtosis. The distribution is defined by a power transformation Y v . The Box-Cox t Distribution Description. Density, distribution function, quantile function, and random generation for the Box-Cox t distribution with parameters mu, sigma, .
A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are .The function BCT() defines the Box-Cox t distribution, a four parameter distribution, for a gamlss.family object to be used in GAMLSS fitting using the function gamlss() . The functions .
Box-Cox t distribution for fitting a GAMLSS Description. The function BCT() defines the Box-Cox t distribution, a four parameter distribution, for a gamlss.family object to be used in GAMLSS fitting using the function gamlss().
In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution.Extra distributions can be created, by transforming, any continuous distribution defined on the real line, to a distribution defined on ranges 0 to infinity or 0 to 1, by using a ’log’ or a ’logit’ transformation respectively. BCT() returns a gamlss.family object which can be used to fit a Box Cox-t distribution in the gamlss() function. dBCT() gives the density, pBCT() gives the distribution function, qBCT() gives the quantile function, and rBCT() generates random deviates.
The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. The Box–Cox t (BCT) distribution is presented as a model for a dependent variable Y exhibiting both skewness and leptokurtosis. The distribution is defined by a power transformation Y ν.The Box-Cox t (BCT) distribution is presented as a model for a dependent variable Y exhibiting both skewness and leptokurtosis. The distribution is defined by a power transformation Y v having a shifted and scaled (truncated) t distribution with degrees of freedom parameter τ. The Box-Cox t Distribution Description. Density, distribution function, quantile function, and random generation for the Box-Cox t distribution with parameters mu, sigma, lambda, and nu. Usage
A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are able to run a broader number of tests.The function BCT() defines the Box-Cox t distribution, a four parameter distribution, for a gamlss.family object to be used in GAMLSS fitting using the function gamlss() . The functions dBCT , pBCT , qBCT and rBCT define the density, distribution function, quantile function and random generation for the Box-Cox t distribution. [The function .Box-Cox t distribution for fitting a GAMLSS Description. The function BCT() defines the Box-Cox t distribution, a four parameter distribution, for a gamlss.family object to be used in GAMLSS fitting using the function gamlss().In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution.
Extra distributions can be created, by transforming, any continuous distribution defined on the real line, to a distribution defined on ranges 0 to infinity or 0 to 1, by using a ’log’ or a ’logit’ transformation respectively. BCT() returns a gamlss.family object which can be used to fit a Box Cox-t distribution in the gamlss() function. dBCT() gives the density, pBCT() gives the distribution function, qBCT() gives the quantile function, and rBCT() generates random deviates.
The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. The Box–Cox t (BCT) distribution is presented as a model for a dependent variable Y exhibiting both skewness and leptokurtosis. The distribution is defined by a power transformation Y ν.The Box-Cox t (BCT) distribution is presented as a model for a dependent variable Y exhibiting both skewness and leptokurtosis. The distribution is defined by a power transformation Y v having a shifted and scaled (truncated) t distribution with degrees of freedom parameter τ. The Box-Cox t Distribution Description. Density, distribution function, quantile function, and random generation for the Box-Cox t distribution with parameters mu, sigma, lambda, and nu. Usage

A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are able to run a broader number of tests.
doubly stochastic poisson process

stainless steel garage upper cabinets
$37.40
box-cox-t distribution|cox regression equation