normal distribution on a box plot A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum. The box part of . Type 2 Enclosures constructed for indoor use to provide a degree of protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects (falling dirt); and
0 · skewed to the right boxplot
1 · positively skewed distribution box plot
2 · positively skewed box plots
3 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
4 · how to interpret boxplot results
5 · boxplot skewed to the left
6 · box and whiskers chart explained
7 · 25th percentile on a boxplot
$3.99

skewed to the right boxplot
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary .Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .Although box plots may seem more primitive than histograms or kernel density estimates, they do have a number of advantages. First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in parallel (see Figure 1 f.
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum. The box part of . Often referred to as a bell curve when plotted on a graph, data with a normal distribution tends to accumulate around a central value; the frequency of values above and below the center decline symmetrically. How is the normal .One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would .
Review of box plots, including how to create and interpret them. Normal quantile plot (or normal probability plot): This plot is provided through statistical software on a computer or graphing calculator. If the points lie close to a line, the data comes from a distribution that is . Which method of the three: histogram, box plot and probability plot is best at determining whether a distribution is approximately normally distributed? Why? Using a box plot. A box plot for a normal distribution shows that the mean is the same as the median. It also shows that the data has no extreme values. The data will be symmetrical. Take a look at the two box plots in .
Today, I wanted to talk about a somewhat maligned form of data visualization: the box plot. What are box plots? . The data may look like it follows a normal distribution when presented in a box . This video points out the possible connection between a symmetric box and whisker plot and the normal distribution.It is less easy to justify a box plot when you only have one group’s distribution to plot. Box plots offer only a high-level summary of the data and lack the ability to show the details of a data distribution’s shape. . Under the normal distribution, the distance between the 9th and 25th (or 91st and 75th) percentiles should be about the .
$\begingroup$ I find it a little perverse that many textbooks indicate distributions by box plots when ANOVA is being discussed. In this example, and often, it is easy to see that means will be close to the medians, and to make guesses about heteroscedasticity, but ANOVA deals with means and SDs, not medians and IQRs. $\endgroup$ I am not sure whether the points are Scatter plot. And it is easy to draw points. So I just plot the box chart with norm distribution curve. It is mainly based on Rotated Normal Distribution and some boxplot settings can be found in chapter 5.12.1 of Manual.
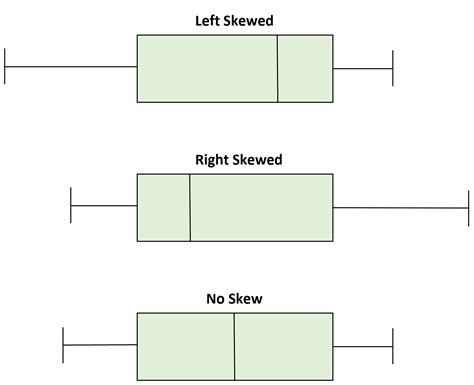
Outlier : If a value is higher than Q3 + 1.5*(Q3-Q1), the value will be considered as outlier.Similarly, if a value is lower than Q1 - 1.5*(Q3-Q1), the value will be considered as outlier.Here Q1 and Q3 are first and third quartile. Normal Distribution : If a box plot has equal proportions around the median, we can say distribution is symmetric or normal.
The following plot shows a boxplot of data with a normal distribution and a box plot of data with a log normal distribution. The plots show that the distribution between the data points is different. The first and second quartiles are very short compared to the first and second quartiles of the normal distribution example, and compared to the .

What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. . highlighting that the data are skewed and that the data are not from a normal distribution. Box plots highlight outliers. Box plots help you identify interesting data points, or outliers. These values are plotted as data points and fall beyond the whiskers.
I'm working with a data-set, so far i have made a histogram with a overlayed normal distribution curve. I want to mark out the quartiles as in this image (the box plot is for reference). This is the code i'm working with:Applications of Box Plots in Medicine. In the medical field, box plots are commonly used to visualize various types of data, such as patient outcomes, laboratory results, and treatment effects. . Normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution, is a key concept in statistics that is widely used in various fields, including .Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.The graph below shows a standard normal probability density function ruled into four quartiles, and the box plot you would expect if you took a very large sample from that distribution. The centre line of the box is the sample median and will estimate the median of the distribution, which is, of course, 0 in this example.
It has a different use. Normally I'd overlay a normal distribution on a histogram. A box plot can be used to compare data that aren't normally distributed. The intent behind box plots is to get an idea of where most of the data are and visualize if some data are quite far away, depending on how the whiskers are determined.
positively skewed distribution box plot
What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. . highlighting that the data are skewed and that the data are not from a normal distribution. Box plots highlight outliers. Box plots help you . The image above is a comparison of a boxplot of a nearly normal distribution and the probability density function (pdf) for a normal distribution. The reason why I am showing you this image is that looking at a statistical distribution is more commonplace than looking at a box plot. In other words, it might help you understand a boxplot.
Instructions: This Normal Probability grapher draw a graph of the normal distribution. Please type the population mean \(\mu\) and population standard deviation \(\sigma\), and provide details about the event you want to graph (for the standard normal distribution , the mean is \(\mu = 0\) and the standard deviation is \(\sigma = 1\)):Let Z be a standard normal random variable and recall the calculations necessary to construct a box plot. (Drag- and-drop your answers to the appropriate boxes for parts (a) to (e) on the given boxplot image.) a) Find the first Q, and third quartiles Q3 for a standard normal distribution. b) Find the inner fences (I F; and. IF.) for a standard .Box Chart with Normal Distribution Curve. Select required data. From the menu, select Plot > Statistical: Box Normal. Half Box with Data Points. Select required data. From the menu, select Plot > Statistical: Half Box. Please see more details on creating and customizing box charts in the Creating Box Charts page. PS. I also have a box plot: normal-distribution; python; nonparametric; qq-plot; shapiro-wilk-test; Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow . best any test can tell you is that according to the test statistic data do not deviate from what is expected under the normal distribution, but data may not be normal anyway (for example due to not .
I am trying to know if the below box-plot represents a normal distribution or if its similar to a normal but i have some doubts about it. The median is 2.0, mean is 2.5 and sd is 1.60. Although the box is symmetric the lengths of whisker are not also mean is not equal to median so i would say this is not similar to a gaussian distribution but i .What relationship exists between the standard normal distribution and the box-plot methodology for describing distributions of data by means of quartiles? The answer depends on the true underlying probability distribution of the data. Assume for the remainder of this exercise that the distribution is normal. Complete parts a through e below. a. Normal Distribution or Symmetric Distribution: If a box plot has equal proportions around the median and the whiskers are the same on both sides of the box then the distribution is normal. Positively Skewed : A distribution is positively skewed when the median is closer to the bottom quartile (Q1).
I would like to plot my data in a bell curve / normal distribution plot and save this as a picture/pdf file for each Name in my dataframe. I have tried to plot the zscores like below: df['by_name'].plot(kind='hist', normed=True) range = np.arange(-7, 7, 0.001) plt.plot(range, norm.pdf(range,0,1)) plt.show() . I have some already tabulated survey data imported in a data frame and can making bar charts from it with ggplot. X X.1 X.2 3 Less than 1 year 7 4 1-5 years 45 5 6-10 years 84 6 11-15 years 104 7 16 or more years 249 Another way to create a normal distribution plot in R is by using the ggplot2 package. Here are two examples of how to create a normal distribution plot using ggplot2. Example 1: Normal Distribution with mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1. To create a normal distribution plot with mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1, we can use the following code:
1927 model t ford turtle deck sheet metal
Choose from our selection of 90 degree brackets, including structural framing, brackets, and more. In stock and ready to ship.
normal distribution on a box plot|25th percentile on a boxplot